In the dynamic world of project management, understanding and mastering key project management topics is crucial for successful project delivery. From initiating a project to closing it out, various facets come into play, each with its own significance and impact on project outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore a diverse range of important project management topics that project managers and aspiring professionals should focus on to enhance their skills and excel in their project endeavors. By gaining knowledge and proficiency in these topics, individuals can navigate challenges, mitigate risks, and ensure the successful completion of projects.
Table of Contents
Introduction:
Project management topics encompass a wide range of areas that are fundamental to effective project planning, execution, and control. These topics provide project managers with the necessary tools, techniques, and insights to manage projects efficiently, deliver quality outcomes, and meet stakeholders’ expectations. From scope management and risk management to communication management and stakeholder management, each topic plays a critical role in the overall success of a project. By delving into these project management topics, professionals can develop a holistic understanding of the intricacies involved in project management, enabling them to make informed decisions, drive collaboration, and effectively lead project teams.

Understanding and prioritizing the important project management topics is key to ensuring a solid foundation in project management practices. These topics have been identified as critical areas that project managers must be proficient in to handle the complexities of projects successfully. They encompass both technical knowledge, such as time management and cost management, and essential soft skills, including leadership and communication. By recognizing the importance of these project management topics and investing time and effort into learning and mastering them, professionals can enhance their project management capabilities and increase their chances of delivering projects on time, within budget, and to the satisfaction of stakeholders.
By focusing on these important project management topics, professionals can equip themselves with the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in their project management endeavors and drive successful project outcomes.
Agile Project Management
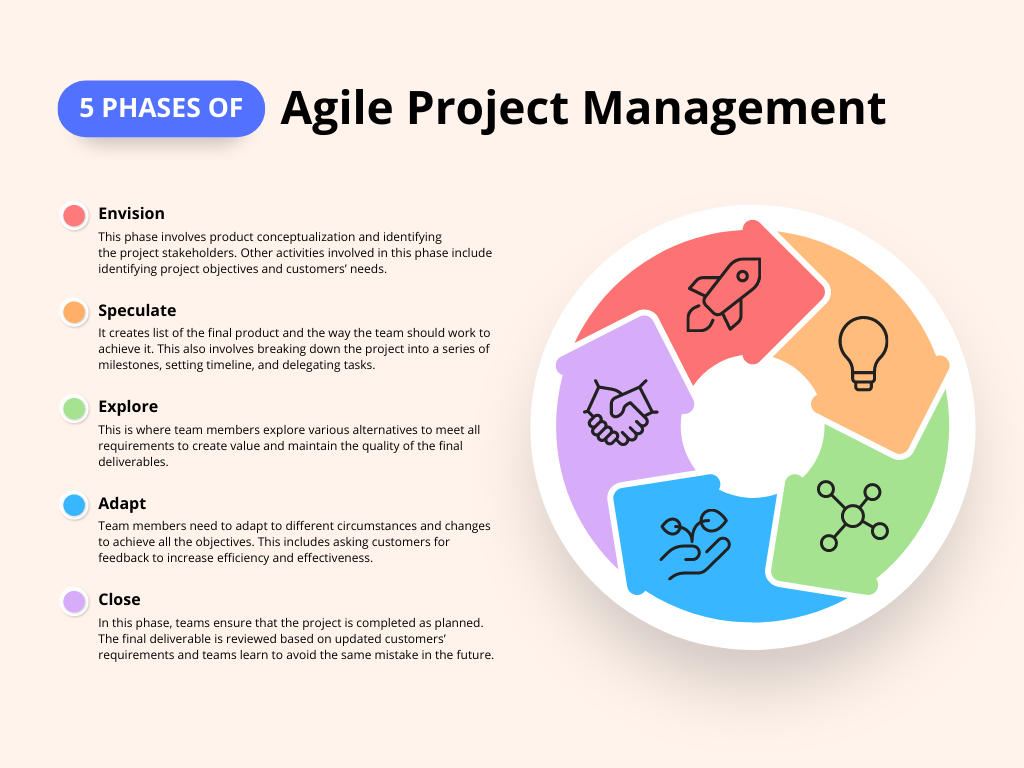
Agile Project Management is an iterative and collaborative approach that prioritizes flexibility and adaptability. Unlike traditional project management methods, Agile emphasizes delivering value in small increments through frequent iterations called sprints. This approach enables teams to respond to changing requirements and customer feedback more effectively, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and improved project outcomes. Agile Project Management relies on the principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto, which values individuals and interactions, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change. By embracing Agile, project teams can foster better communication, encourage self-organization, and deliver valuable products or services that meet customer needs.
Project Scope Management
Scope of the Project Management is the process of defining and controlling what is included and excluded in a project. It encompasses activities such as gathering requirements, establishing project boundaries, and managing scope changes throughout the project lifecycle. Effectively managing project scope is crucial for project success, as it ensures that the project team and stakeholders have a shared understanding of project objectives and deliverables. By clearly defining the scope, project managers can set realistic expectations, allocate resources appropriately, and avoid scope creep, which refers to uncontrolled changes or additions to the project scope. Through careful scope management, project teams can maintain focus, control project costs and timelines, and increase the likelihood of delivering a successful outcome that meets stakeholders’ expectations.
Project Risk Management
Risk of the Project Management involves identifying, analyzing, and responding to potential risks that may impact project objectives. It is a proactive process that helps project teams anticipate and mitigate risks before they become significant issues. Risk identification involves systematically identifying potential risks that may arise during the project, considering internal and external factors that can impact the project’s success. Risk analysis involves assessing the likelihood and impact of identified risks to prioritize them for further attention. Risk response planning involves developing strategies to minimize or eliminate risks, such as risk avoidance, risk mitigation, risk transfer, or risk acceptance. By effectively managing project risks, project teams can enhance project outcomes, reduce surprises, and make informed decisions to protect project success.

Project Communication Management
Communication in the Project Management involves the systematic planning, execution, and monitoring of project-related communications. Effective communication is crucial for project success as it facilitates the exchange of information, fosters collaboration, and ensures stakeholders are informed and engaged throughout the project. This includes developing a communication plan that outlines the project’s communication objectives, target audience, and preferred communication methods. Project managers must also establish clear channels for sharing project updates, addressing concerns, and managing conflicts. By maintaining open lines of communication, project teams can enhance stakeholder relationships, build trust, and align project activities with organizational goals.
Project Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder in the part of Project Management involves identifying, analyzing, and engaging stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle to ensure their needs and expectations are understood and addressed. It includes activities such as stakeholder identification, stakeholder analysis, stakeholder communication, and stakeholder engagement. Stakeholder identification involves identifying all individuals, groups, or organizations who have an interest in or are affected by the project. Stakeholder analysis helps assess their influence, interests, and potential impact on the project. Effective stakeholder communication involves developing appropriate communication strategies and channels to engage stakeholders, gather their input, and keep them informed about project progress. Stakeholder engagement focuses on actively involving stakeholders in decision-making, addressing their concerns, and fostering positive relationships. By effectively managing project stakeholders, project teams can gain support, mitigate conflicts, and achieve stakeholder satisfaction, which ultimately contributes to project success.

Project Time Management
Time of Project Management involves the processes and techniques used to effectively plan, schedule, and control project activities. It encompasses activities such as defining project milestones, sequencing tasks, estimating durations, and developing project schedules. By carefully managing project time, project managers can ensure that activities are completed in a timely manner, resources are allocated efficiently, and deadlines are met. Time management techniques such as critical path analysis, schedule compression, and resource leveling help identify dependencies, optimize resource utilization, and address schedule constraints. Through effective time management, project teams can stay on track, proactively manage delays, and deliver projects within the agreed-upon timeframes.

Project Cost Management
Cost of the Project Management involves estimating, budgeting, and controlling project costs throughout the project lifecycle. It includes activities such as cost estimation, cost budgeting, and cost control. Cost estimation involves predicting the resources and expenses required to complete project activities, while cost budgeting involves allocating the estimated costs to different project components. Cost control involves monitoring and managing project expenditures to ensure they align with the approved budget. Project managers use techniques such as bottom-up estimation, parametric estimation, and earned value management to accurately estimate and track project costs. Effective cost management allows project teams to optimize resource allocation, manage project finances, and make informed decisions to keep projects within budget.

Project Quality Management
Project Quality Management involves planning, executing, and controlling activities to ensure that project deliverables meet established quality standards and stakeholder expectations. It encompasses processes such as quality planning, quality assurance, and quality control. Quality planning involves identifying quality objectives, determining quality requirements, and developing a quality management plan. Quality assurance focuses on systematic processes and activities to ensure that project activities are being performed as planned and that deliverables meet defined quality standards. Quality control involves monitoring and inspecting project deliverables to identify and address any deviations from the quality requirements. By prioritizing and implementing effective quality management practices, project teams can enhance customer satisfaction, minimize rework, and improve overall project performance.
Project Integration Management
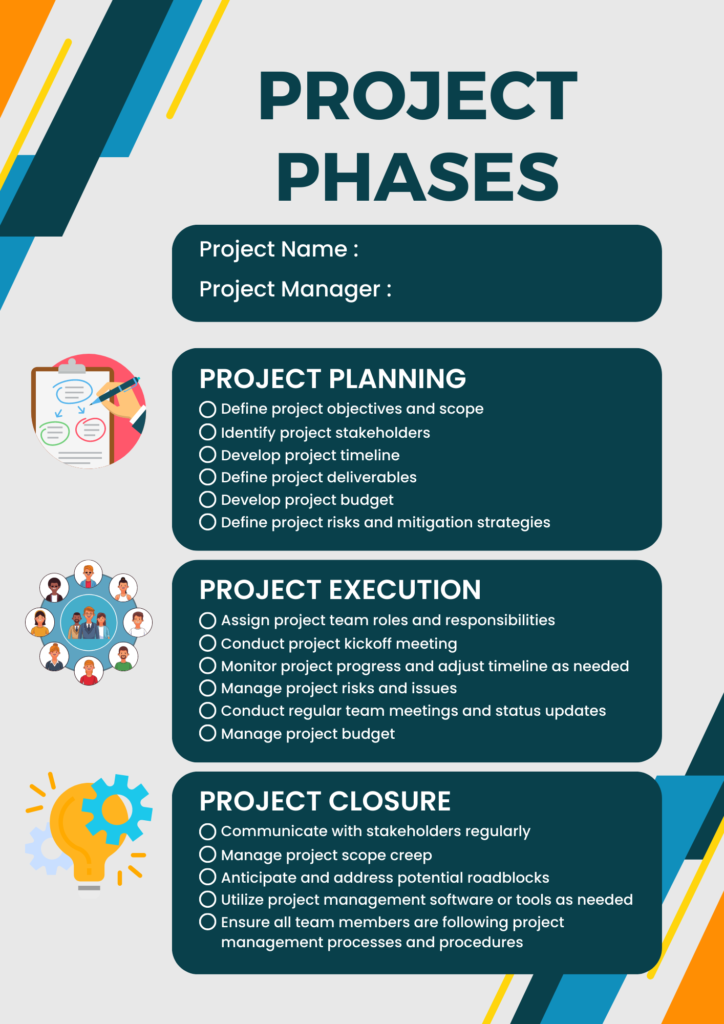
Project Integration Management involves coordinating and integrating various project processes, activities, and components to ensure project success. It includes activities such as project initiation, project planning, project execution, project monitoring and control, and project closure. Project integration management serves as the glue that brings all project elements together, ensuring alignment with project objectives, stakeholder expectations, and organizational strategies. It involves creating and maintaining project documents, performing change control, facilitating communication and collaboration among project stakeholders, and overseeing overall project progress. By effectively managing project integration, project managers can ensure that project activities are well-coordinated, deliverables are integrated, and the project as a whole stays on track toward achieving its intended outcomes.
Project Leadership and Team Management
Project Leadership and Team Management involve leading and motivating project teams to achieve project objectives effectively. It encompasses activities such as team formation, team development, and team performance management. Strong project leadership involves setting a clear project vision, establishing goals, and providing guidance and direction to the team. It also involves effective communication, conflict resolution, and decision-making. Team management focuses on creating a collaborative and supportive team environment, fostering trust and open communication, and empowering team members to contribute their skills and expertise. By fostering effective project leadership and team management, project managers can inspire high performance, boost team morale, and drive project success.

Project Procurement Management
Project Procurement Management involves planning, executing, and controlling the procurement activities required to acquire goods and services from external vendors or suppliers. It encompasses processes such as procurement planning, solicitation planning, solicitation, source selection, contract administration, and contract closure. Procurement planning involves determining what needs to be procured, developing procurement strategies, and identifying potential suppliers. Solicitation planning focuses on preparing the procurement documents and selecting the appropriate procurement methods. During solicitation, requests for proposals or bids are sent to potential suppliers, who then submit their proposals. Source selection involves evaluating and selecting the most suitable supplier based on predefined criteria. Contract administration involves managing the relationship with the supplier, monitoring contract performance, and resolving any issues that may arise. Effective procurement management ensures that project teams have the necessary resources and deliverables from external sources, and that contracts are executed and administered in a fair and efficient manner.
Project Change Management
Project Change Management involves identifying, assessing, and managing changes that occur throughout the project lifecycle. It encompasses processes such as change identification, change impact analysis, change approval, change implementation, and change control. Change identification involves recognizing potential changes to project scope, schedule, budget, or other components. Change impact analysis assesses the effects of proposed changes on the project, considering factors such as risks, costs, and resources. Change approval involves evaluating and approving or rejecting change requests based on their potential impact and alignment with project objectives. Change implementation focuses on executing approved changes, updating project documents, and communicating changes to relevant stakeholders. Change control involves monitoring and controlling changes to ensure they are executed properly, minimizing risks, and avoiding scope creep. Effective change management ensures that changes are carefully assessed, controlled, and implemented, minimizing disruptions and maximizing project success.
Project Schedule Management
Project Schedule Management involves the processes and techniques used to develop, manage, and control the project schedule. It encompasses activities such as defining project activities, sequencing them, estimating their durations, and creating a project schedule. Developing a project schedule involves breaking down the work into manageable tasks, identifying dependencies between activities, and determining the order in which they should be executed. Estimating activity durations requires considering historical data, expert judgment, and input from the project team. Once the schedule is developed, project managers use techniques like critical path analysis and schedule compression to optimize the timeline and identify critical activities. Throughout the project, schedule control involves monitoring progress, addressing deviations, and adjusting the schedule as necessary. Effective schedule management ensures that the project is completed on time, enables resource allocation, and helps manage stakeholder expectations.
Project Resource Management
Project Resource Management involves effectively identifying, acquiring, and managing the resources required for project execution. It includes activities such as resource planning, resource allocation, and resource optimization. Resource planning involves identifying the types and quantities of resources needed, considering both human resources and physical assets. Resource allocation involves assigning resources to project activities based on their availability, skills, and expertise. It also involves managing potential conflicts or overutilization of resources. Resource optimization aims to maximize resource utilization, minimize waste, and ensure that resources are used efficiently throughout the project. Effective resource management helps ensure that the project has the right people with the right skills, equipment, and materials at the right time. It allows project managers to balance workload, avoid resource bottlenecks, and optimize project performance.
Project Planning and Execution
Project Planning and Execution are crucial phases in project management that involve defining project objectives, creating a detailed project plan, and executing the plan to achieve project deliverables. During the planning phase, project managers work with stakeholders to determine project scope, develop a work breakdown structure, and create a project schedule. They also identify project risks, develop risk mitigation strategies, and establish communication and stakeholder engagement plans. Once the planning is complete, the project moves into the execution phase, where project teams implement the project plan, perform project activities, and monitor progress. Project managers oversee team performance, manage changes, and ensure that the project stays on track. Effective planning and execution lay the foundation for project success by providing clear direction, aligning activities with project goals, and enabling effective project control and coordination.
Project Closure
Project Closure is the final phase of the project lifecycle, where project activities are formally completed, and the project is closed out. It involves verifying that project deliverables meet acceptance criteria, conducting a final project review, and obtaining sign-off from stakeholders. Project closure also includes documenting lessons learned, conducting post-project evaluations, and archiving project documentation. Additionally, project managers ensure the proper handover of project deliverables to relevant stakeholders and perform financial closure, including final budget reconciliation and contract closure. Effective project closure is essential to formally conclude the project, capture insights for future projects, and transition resources back to their respective areas. It allows organizations to evaluate project success, celebrate achievements, and identify areas for improvement.



