A Guide to Project Risk Management in Project Management
Table of Contents
Introduction
The concept of Project risk management in project management has evolved over time as projects have become more complex and the need for effective risk mitigation has become increasingly crucial. In the early days of project management, risks were often overlooked or dealt with reactively, leading to frequent project failures and costly setbacks.
It was during the 20th century that the formalization of risk management practices began to take shape. The field of project management started recognizing the importance of identifying and managing risks systematically. This shift in mindset was driven by industries such as aerospace, construction, and defense, which faced significant risks and needed robust risk management approaches.
In the 1950s, the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) was developed, introducing a structured method for analyzing project risks. PERT emphasized identifying critical paths, estimating time and cost uncertainties, and developing contingency plans to address potential risks.
In the 1980s, the Project Management Institute (PMI) published the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), which included a dedicated knowledge area on project risk management. This marked a significant milestone in formalizing risk management processes and techniques in project management.
Since then, risk management has become an integral part of project management methodologies, such as the PMBOK Guide and PRINCE2. These frameworks provide guidelines and best practices for identifying, analyzing, and responding to risks throughout the project lifecycle.
Today, risk management in project management has advanced further with the integration of technology and the use of sophisticated risk analysis tools. Project managers are equipped with various techniques, such as risk registers, risk matrices, and Monte Carlo simulations, to effectively assess and address project risks.
Understanding the history of risk management in project management helps us appreciate the progression of practices and the recognition of the critical role that risk management plays in project success. By leveraging historical knowledge and adopting contemporary risk management approaches, project managers can enhance their ability to navigate uncertainties and deliver successful outcomes.
Definition of Risk in Project Management
In project management, risk refers to the potential for an event or condition to occur that could have a positive or negative impact on the project’s objectives. It encompasses uncertainties and the possibility of deviations from the expected outcomes. Risks can arise from various sources, such as technological factors, organizational issues, external influences, or even human errors. By understanding and effectively managing project risks, project managers can enhance their ability to deliver successful outcomes within the defined constraints.
Importance of Identifying and Managing Project Risks
Identifying and managing project risks is a critical aspect of project management. Failure to recognize and address risks can lead to costly consequences, including budget overruns, schedule delays, decreased quality, or even project failure. By proactively identifying and managing risks, project managers can minimize their impact and maximize opportunities for success. Risk management enables project teams to anticipate potential obstacles, allocate resources effectively, make informed decisions, and develop contingency plans to mitigate or respond to risks. It also helps in maintaining stakeholder confidence and ensuring project objectives are achieved.
Purpose of the Blog
The purpose of this blog is to provide a comprehensive guide on identifying project risks and implementing risk management strategies in project management. It aims to equip project managers and teams with the knowledge and tools necessary to proactively assess, prioritize, and address risks throughout the project lifecycle. By following the principles and best practices outlined in this blog, readers will gain valuable insights into identifying potential risks, analyzing their impact, developing appropriate response plans, and monitoring risks to ensure project success.
Understanding Project Risks
Definition of Project Risks
Project risks can be defined as the potential events or conditions that can have an adverse impact on project objectives. These risks encompass both threats and opportunities that may arise during the course of a project. Risks can stem from various factors, including uncertainties in technology, resource limitations, stakeholder conflicts, environmental factors, regulatory changes, or even changes in project requirements. It is important to note that project risks are inherent and cannot be completely eliminated, but they can be effectively managed to minimize their impact and maximize project success.
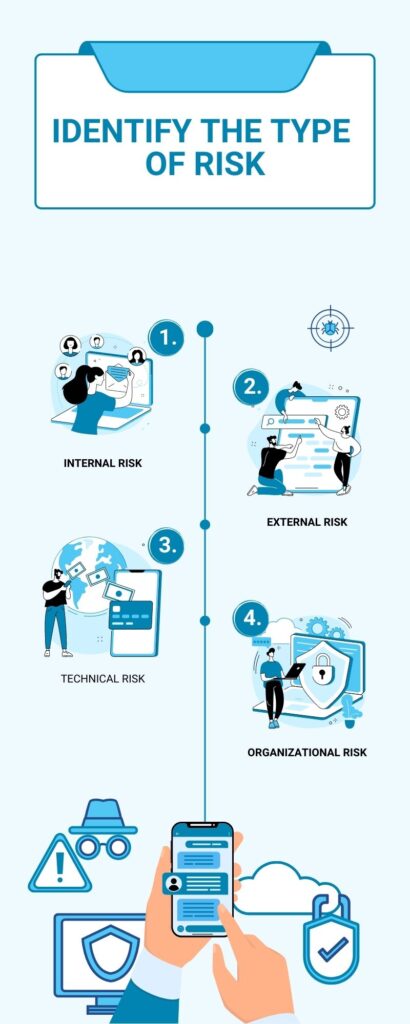
Types of Project Risks
- Internal Risks: These risks arise from within the project and are typically under the control of the project team. Examples include poor project planning, inadequate resource allocation, ineffective communication, or lack of expertise in project management.
- External Risks: External risks originate from factors outside the project team’s control but can still impact the project’s success. These risks may include market fluctuations, changes in government regulations, economic uncertainties, or natural disasters.
- Technical Risks: Technical risks are associated with the project’s technology or the methods used to deliver the project’s objectives. These risks can include technical failures, compatibility issues, security breaches, or challenges in integrating different systems or components.
- Organizational Risks: Organizational risks stem from the internal environment of the organization executing the project. Examples include inadequate project governance, organizational changes, lack of stakeholder support, or conflicting priorities within the organization.
Common Sources of Project Risks
- Unclear Project Objectives: When project objectives are not well-defined or communicated, it can lead to scope creep, confusion, and conflicting expectations, increasing the risk of project failure.
- Inadequate Planning: Poor project planning, including inaccurate estimates, insufficient resource allocation, or lack of contingency plans, can lead to cost overruns, schedule delays, and compromised project outcomes.
- Stakeholder Issues: Conflicts among stakeholders, unrealistic expectations, or lack of stakeholder engagement and support can hinder project progress and create risks to successful project delivery.
- Technology and Complexity: Projects involving complex technologies or intricate systems may encounter technical challenges, compatibility issues, or dependencies on external factors that can introduce risks to project success.
- External Factors: External risks such as market volatility, changes in regulations, political instability, or natural disasters can significantly impact project timelines, costs, and outcomes.
Understanding the different types of project risks and their common sources is crucial for effective risk management. By identifying and assessing these risks, project managers can develop proactive strategies to address them, minimize their impact, and increase the chances of project success.
The Risk Management Process
Step 1: Risk Identification
Techniques for Identifying Project Risks
There are several techniques that project managers can employ to identify project risks effectively:
Brainstorming: Conducting brainstorming sessions with the project team and relevant stakeholders can help generate a wide range of potential risks. This collaborative approach encourages open discussion and idea sharing, allowing for the identification of both obvious and hidden risks.
SWOT Analysis: Conducting a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis can help identify risks by assessing the internal strengths and weaknesses of the project, as well as external opportunities and threats. By considering both positive and negative factors, project managers can uncover risks that may not be immediately apparent.
Risk Checklists: Utilizing pre-defined risk checklists can serve as a helpful tool for systematically identifying potential risks based on past experiences or industry-specific knowledge. These checklists provide a structured approach to ensure comprehensive risk identification.
Importance of Involving Key Stakeholders in the Risk Identification Process
Involving key stakeholders in the risk identification process is essential for several reasons:

Diverse Perspectives: Stakeholders bring unique insights and experiences related to the project. Their involvement ensures a more comprehensive view of potential risks, considering different viewpoints and areas of expertise.
Enhanced Risk Awareness: Engaging stakeholders in risk identification increases their awareness of potential project risks. This shared understanding fosters a risk-aware culture within the project team, encouraging proactive risk management throughout the project lifecycle.
Ownership and Accountability: When stakeholders are actively involved in identifying risks, they feel a sense of ownership and accountability for managing those risks. This leads to better engagement and commitment in implementing risk response strategies.
Early Problem Identification: Stakeholders, particularly those directly impacted by the project, may have specific insights into risks that could impact their interests or objectives. Their involvement in risk identification enables early detection and mitigation of these risks, minimizing potential disruptions.
By leveraging various techniques and involving key stakeholders, project managers can ensure a comprehensive identification of project risks. This proactive approach lays the foundation for effective risk management, enabling the project team to address risks timely and develop appropriate response plans to safeguard project success.
Techniques for Identifying Project Risks
Brainstorming Sessions
Brainstorming sessions involve gathering the project team and relevant stakeholders to generate ideas and identify potential risks. During these sessions, participants freely share their thoughts and perspectives on risks that could impact the project. The collaborative nature of brainstorming encourages creativity and helps uncover both obvious and hidden risks. Facilitated discussions and structured prompts can further stimulate idea generation and ensure a comprehensive identification of risks.
Risk Checklists
Risk checklists are pre-defined lists of potential risks based on past experiences, industry knowledge, or best practices. These checklists serve as a valuable reference tool to prompt project managers and teams to consider risks that may be commonly encountered in similar projects. By systematically reviewing and adapting relevant risk checklists, project teams can ensure a more thorough identification of risks and avoid overlooking critical areas.
Lessons Learned from Similar Projects
Drawing from the lessons learned in previous projects or similar endeavors can provide valuable insights into potential risks. Analyzing the experiences of other projects within the organization or industry can reveal patterns, recurring issues, and risks that were encountered. By leveraging these lessons, project managers can proactively identify and mitigate risks that have been previously encountered, reducing the likelihood of similar setbacks or failures.
Expert Judgment and Consultation
Seeking expert judgment and consultation is an effective way to identify project risks. Engaging subject matter experts, experienced professionals, or consultants who possess specialized knowledge and expertise relevant to the project can help identify risks that may not be immediately apparent. These experts can offer insights, alternative perspectives, and identify risks based on their extensive experience in similar projects or domains.
SWOT Analysis
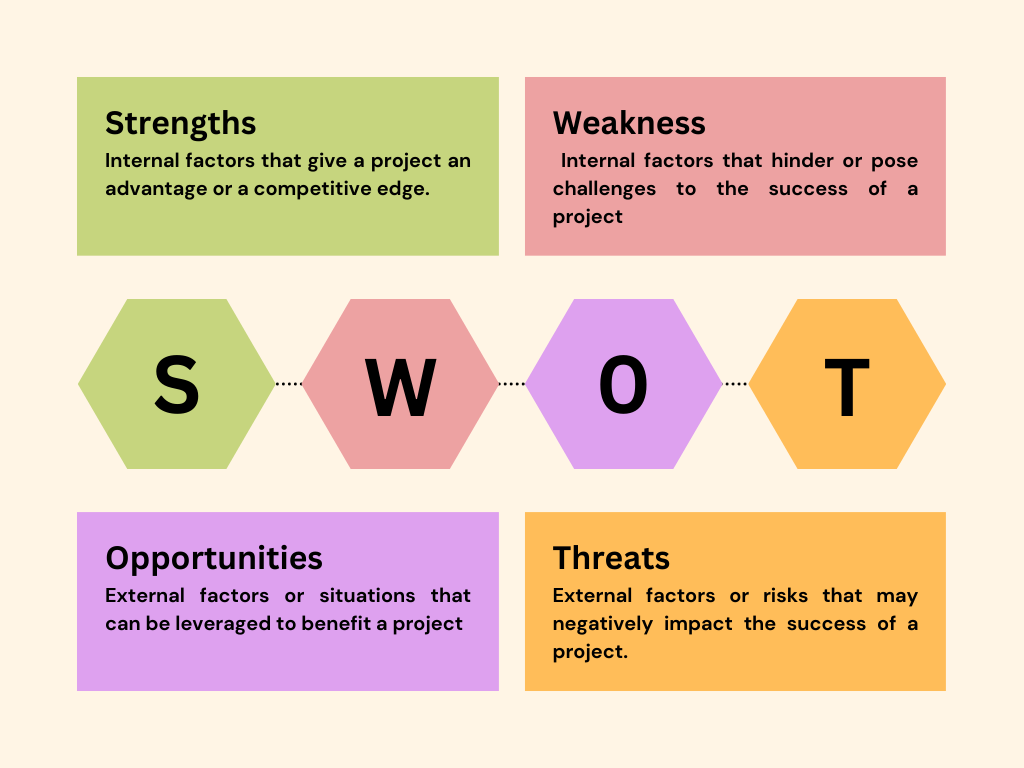
Conducting a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis can aid in the identification of project risks. By evaluating the project’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats, project teams can assess risks from a holistic perspective. SWOT analysis enables project managers to identify risks related to project vulnerabilities (weaknesses), external factors that could pose risks (threats), and potential risks stemming from unexplored opportunities.
By employing these techniques, project managers can systematically identify project risks and increase their understanding of potential challenges and opportunities. Utilizing a combination of brainstorming, risk checklists, lessons learned, expert judgment, and SWOT analysis allows for a comprehensive and robust risk identification process, setting the stage for effective risk management throughout the project lifecycle.
Best Practices for Effective Risk Management
Cultivating a Risk-Aware Culture within the Project Team
Fostering a risk-aware culture within the project team is essential for effective risk management. This involves creating an environment where team members understand the importance of identifying and addressing risks throughout the project lifecycle. Encouraging proactive risk identification, open discussions about potential risks, and promoting a sense of shared responsibility for risk management enhances the team’s ability to anticipate and respond to risks effectively.
Encouraging Open Communication and Collaboration
Open communication and collaboration are vital for successful risk management. Project managers should promote an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their concerns, ideas, and insights regarding project risks. Encouraging regular communication channels, such as team meetings, risk review sessions, or dedicated risk management workshops, facilitates the exchange of information and enables collaborative decision-making to address identified risks.
Regularly Reviewing and Updating Risk Management Plans
Risk management plans should not be static documents. They should be dynamic and subject to regular review and updates throughout the project lifecycle. Project managers should allocate dedicated time and resources to assess and reassess project risks, evaluate the effectiveness of risk responses, and identify new risks that may emerge. By keeping risk management plans current and relevant, project teams can proactively address risks and adapt their strategies as the project progresses.
Monitoring External Factors That May Impact the Project
External factors beyond the project team’s control can significantly impact project risks. Project managers should actively monitor and stay informed about external influences such as market conditions, regulatory changes, technological advancements, or political developments. This awareness allows for timely risk identification and appropriate adjustments to risk management plans and strategies to mitigate potential impacts.
Conducting Risk Assessments at Different Project Stages
Risk assessments should be conducted at various stages of the project. Identifying risks early in the project lifecycle allows for proactive planning and implementation of risk responses. As the project progresses, reassessing risks helps ensure that new risks are identified and existing risks are managed effectively. Regular risk assessments enable project managers to stay ahead of potential threats and take necessary actions to minimize their impact on project objectives.
By implementing these best practices, project managers can establish a robust risk management approach. Cultivating a risk-aware culture, promoting open communication, regularly reviewing risk management plans, monitoring external factors, and conducting risk assessments at different project stages contribute to proactive risk management and enhance the project’s chances of success.
Case Studies: Real-life Examples of Project Risks and Management
Example 1: Software Development Project
In a software development project, one common risk is the emergence of technical challenges. For instance, consider a project where a team is developing a new mobile application. During the development process, they encounter compatibility issues between the application and different operating systems, resulting in unexpected crashes and functionality limitations. To mitigate this risk, the project team can implement a thorough testing and quality assurance process, conducting extensive compatibility testing across various platforms and versions. By proactively addressing this risk, they can ensure a stable and user-friendly application, enhancing customer satisfaction and minimizing the need for post-launch bug fixes.
Example 2: Construction Project
In a construction project, unforeseen site conditions can pose significant risks. For example, a project involving the construction of a high-rise building may encounter unexpected soil instability, requiring additional foundation reinforcement. To manage this risk, the project team can conduct thorough site surveys and soil testing before construction begins. By leveraging geotechnical expertise, they can accurately assess the soil conditions and adjust the project design and construction plan accordingly. This proactive approach minimizes the potential for costly delays and structural issues during the construction phase.
Example 3: Marketing Campaign
In a marketing campaign, market dynamics and changing consumer behavior can present risks. For instance, imagine a company launching a new product with a digital marketing campaign. One risk they may face is the potential for negative online reviews or backlash on social media platforms. To manage this risk, the marketing team can establish a robust online reputation management strategy. This involves monitoring online conversations, promptly addressing customer feedback, and implementing proactive measures to mitigate and resolve any potential issues. By actively managing their online presence and engaging with customers, the company can maintain a positive brand image and minimize the impact of negative sentiment on their campaign’s success.
Including flow diagrams and images in case studies can provide visual representations of the risks and their management strategies. For example, in the software development case study, a flow diagram could illustrate the testing process, highlighting the specific steps taken to address compatibility issues. In the construction project case study, an image depicting the soil testing and foundation reinforcement process can enhance understanding of the risk management approach. Similarly, in the marketing campaign case study, visual representations, such as screenshots of social media engagement or a timeline of online reputation management activities, can illustrate the proactive measures taken to mitigate risks. These visuals enhance the readability and engagement of the case studies, enabling readers to better grasp the real-life examples of project risks and their management.
Conclusion
Recap of the Importance of Identifying and Managing Project Risks
Identifying and managing project risks is crucial for successful project management. By proactively identifying risks, project teams can anticipate potential obstacles, allocate resources effectively, and develop strategies to mitigate or respond to risks. Failure to address risks can lead to cost overruns, schedule delays, compromised quality, and even project failure. Therefore, recognizing the importance of identifying and managing project risks is paramount for achieving project objectives and ensuring overall project success.

Key Takeaways for Effective Risk Management in Project Management
Effective risk management involves several key practices:

- Proactive Identification: Utilize various techniques, such as brainstorming sessions, risk checklists, lessons learned, expert judgment, and SWOT analysis, to identify potential risks comprehensively.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Engage key stakeholders in the risk identification process to benefit from their diverse perspectives and ensure ownership and accountability in risk management.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly review and update risk management plans to adapt to evolving project conditions and external factors that may impact project risks.
- Cultivate a Risk-Aware Culture: Foster a risk-aware culture within the project team, encouraging open communication, collaboration, and a shared responsibility for risk management.
- Conduct Risk Assessments: Conduct risk assessments at different stages of the project to identify new risks and reassess existing risks, allowing for timely mitigation and response.
Encouragement to Apply the Outlined Strategies to Future Projects
In conclusion, effective risk management is a critical aspect of project management that cannot be overlooked. By applying the strategies and best practices outlined in this blog, project managers and teams can enhance their ability to identify, analyze, and respond to project risks. It is important to proactively manage risks throughout the project lifecycle, adapting risk management plans as needed and involving stakeholders in the process. By doing so, project teams can minimize the impact of risks, increase project success rates, and deliver desired outcomes. Embracing a risk management mindset and applying these strategies to future projects will contribute to the overall success of project endeavors.



