Risk management is a fundamental process that organizations undertake to identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks that may impact their operations, projects, or objectives. It is essential for several reasons. Firstly, risk management helps organizations proactively anticipate and address uncertainties, minimizing the likelihood of negative outcomes and maximizing opportunities. By identifying and understanding risks, organizations can make informed decisions and take appropriate actions to protect their assets, reputation, and overall business continuity.
Secondly, risk management enables organizations to optimize resource allocation and enhance performance. By assessing and prioritizing risks, organizations can allocate resources effectively to address the most critical risks. This ensures that efforts and investments are focused on areas with the highest potential impact. Risk management also facilitates effective decision-making by providing a systematic framework for evaluating risks and their potential consequences.
When it comes to risk management, it should be an ongoing and integrated process. Organizations should continuously monitor and assess risks, adapting their strategies as new risks emerge or existing risks evolve. Risk management should be embedded in the culture and operations of the organization, involving all stakeholders and departments. It should be integrated into project management, operational processes, and strategic planning to ensure a comprehensive and cohesive approach to risk mitigation. Ultimately, risk management enables organizations to navigate uncertainties, protect their interests, and achieve their objectives with greater confidence and resilience.
Table of Contents
I. Introduction to Project Risk Management
A. Definition of project risk management
Project risk management is the systematic process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that can impact the successful outcome of a project. It involves proactive measures to anticipate and address uncertainties, ensuring that projects are delivered within scope, budget, and schedule. Risk management is an integral part of project management, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions to minimize or eliminate threats to project objectives. By systematically analyzing risks, project teams can better understand the potential pitfalls and develop effective strategies to mitigate them.
B. Importance of project risk management
Effective project risk management is paramount for achieving project success. It provides a structured approach to identify, assess, and respond to risks, which helps in minimizing project failures, cost overruns, and delays. By considering potential risks upfront, organizations can make informed decisions, allocate resources efficiently, and enhance the overall project performance. Risk management enables project teams to proactively identify and address issues, reducing the likelihood of surprises or unexpected setbacks during project execution. Moreover, it fosters stakeholder confidence by demonstrating a proactive approach to risk mitigation, which can positively impact the organization’s reputation and client satisfaction.
C. Overview of the risk management process
The risk management process involves several interconnected stages to effectively manage project risks. It begins with risk identification, where potential risks are identified through techniques such as brainstorming sessions, documentation reviews, and expert judgment. The next step is risk assessment and analysis, which evaluates the probability and impact of each risk and prioritizes them based on their significance. This helps in focusing efforts on the most critical risks that require immediate attention.
Once risks are identified and assessed, the project team develops risk response plans. These plans outline specific strategies for addressing each risk, including avoidance, mitigation, transfer, or acceptance. Risk monitoring and control play a crucial role throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring that risks are regularly assessed, tracked, and appropriate actions are taken to control or mitigate them. Effective communication and reporting of risks to stakeholders are essential, as it enables informed decision-making and promotes transparency.
In summary, project risk management is a vital process that enables organizations to anticipate, address, and minimize potential risks that can impact project success. By systematically identifying and addressing risks, project teams can enhance project outcomes, manage uncertainties, and deliver projects successfully.
II. Risk Identification
A. Identifying project risks.
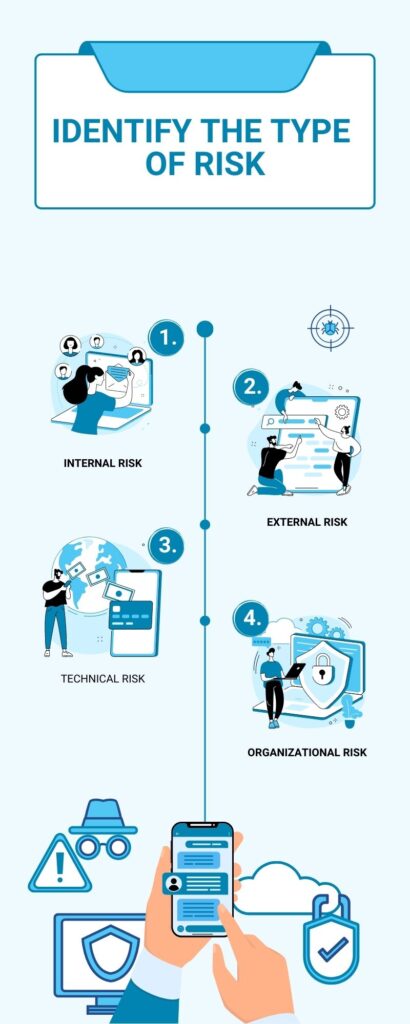
In order to effectively manage risks, it is crucial to identify the various types of risks that can potentially impact a project. Project risks can be categorized into four main types: internal risks, external risks, technical risks, and organizational risks.
- Internal risks refer to risks that originate within the project itself or the organization executing the project. These risks can include inadequate resources, skill gaps within the team, poor project planning, or ineffective communication among project stakeholders.
- External risks are risks that arise from external factors outside the control of the project team. These risks can include changes in market conditions, regulatory changes, economic uncertainties, or natural disasters that may impact project timelines, budgets, or resources.
- Technical risks are associated with the specific technology or processes being used in the project. These risks can arise from technical complexities, software or hardware failures, compatibility issues, or insufficient technical expertise within the project team.
- Organizational risks pertain to risks that stem from the structure, culture, or policies of the organization executing the project. These risks can include inadequate project governance, lack of management support, conflicting priorities, or resistance to change.
B. Techniques for identifying risks.
Identifying project risks requires a systematic approach to ensure comprehensive coverage. Several techniques can be utilized to identify risks effectively:
- Brainstorming sessions: This involves bringing together project team members and stakeholders to generate ideas and identify potential risks. By encouraging open discussion and collaboration, different perspectives and insights can be gathered, leading to the identification of a wide range of risks.
- Documentation review: Reviewing project documentation such as project plans, requirements, previous project reports, and lessons learned can provide valuable insights into potential risks. Analyzing historical data and project documentation can help identify patterns, recurring issues, or areas that have been prone to risks in the past.
- Expert judgment: Seeking input from subject matter experts, experienced project managers, or individuals with domain-specific knowledge can greatly enhance the identification of risks. These experts can provide valuable insights and perspectives based on their experience, helping to identify risks that may not be apparent to the project team.
By utilizing these techniques, project teams can systematically identify a wide range of risks across different categories, ensuring a comprehensive risk identification process. This enables the project team to move forward with a clearer understanding of potential threats and opportunities that may affect project success.
III. Risk Assessment and Analysis
A. Qualitative risk analysis
Qualitative risk analysis is a process of evaluating risks based on their probability of occurrence and potential impact on the project. It involves assessing risks qualitatively rather than assigning specific numerical values. The following steps are involved in qualitative risk analysis:
- Assessing the probability and impact of risks: Risks are evaluated based on their likelihood of occurrence and the potential consequences they can have on the project objectives. Probability can be classified as low, medium, or high, while impact can be categorized as minor, moderate, or major. By considering both factors, risks can be evaluated and ranked based on their overall severity.
- Prioritizing risks using a risk matrix: A risk matrix is a valuable tool for prioritizing risks. It utilizes a grid-like structure that maps the probability and impact ratings of risks to determine their priority levels. Risks falling into high-probability and high-impact quadrants are considered top priorities and require immediate attention, while risks in low-probability and low-impact quadrants may be of lower concern.

B. Quantitative risk analysis
Quantitative risk analysis involves assigning numerical values to risks and utilizing statistical techniques to evaluate and quantify their potential impact on the project. It provides a more detailed and precise assessment of risks. The following steps are involved in quantitative risk analysis:
- Assigning numerical values to risks: Quantitative analysis involves assigning specific values to the probability and impact of risks, often using a scale or probability distribution. This allows for a more precise measurement and calculation of the risks’ potential impact on project objectives.
- Using statistical techniques to evaluate risks: Statistical techniques, such as Monte Carlo simulation, can be applied to analyze the numerical data assigned to risks. This simulation generates multiple iterations of the project, considering different combinations of risk outcomes. By running these simulations, the likelihood of achieving specific project outcomes can be estimated, providing insights into the overall project risk exposure and potential schedule or budget variances.
By conducting qualitative and quantitative risk analysis, project teams can gain a comprehensive understanding of the risks they face. Qualitative analysis helps prioritize risks based on their overall severity, while quantitative analysis provides a more detailed evaluation of the risks’ potential impact. Together, these analyses assist project teams in making informed decisions about risk response strategies and allocating appropriate resources for risk mitigation.
IV. Risk Response Planning
A. Risk response strategies
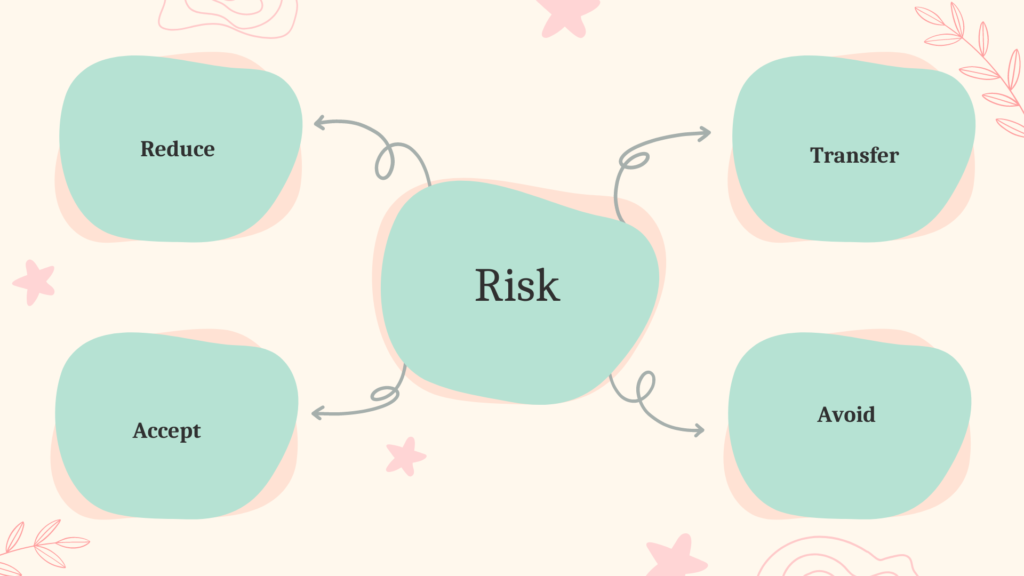
Risk response planning involves developing strategies to address identified risks. There are four main risk response strategies that project teams can employ:
- Avoidance: This strategy aims to eliminate or minimize the probability of a risk occurring. It involves taking proactive measures to change project plans, processes, or conditions to avoid the risk altogether. For example, if a project involves a high-risk vendor, the project team may decide to avoid the risk by selecting a different vendor with a proven track record.
- Mitigation: Mitigation involves reducing the probability or impact of a risk. It focuses on implementing actions to minimize the likelihood of the risk occurring or reducing its potential consequences. This may include implementing additional safety measures, conducting thorough testing, or developing contingency plans. For instance, if there is a risk of software failure, the team may implement rigorous testing protocols to mitigate the potential impact on the project.
- Transfer: Risk transfer involves shifting the responsibility or impact of a risk to a third party, such as an insurance provider or a subcontractor. This strategy is often used when the risk is beyond the project team’s control or when it is more cost-effective to transfer the risk to another party. For example, a construction project may transfer the risk of accidents or property damage to an insurance company.
- Acceptance: Acceptance is a strategy where the project team acknowledges the existence of a risk but chooses not to take any specific action to address it. This approach is typically taken when the potential impact of the risk is minimal or when the cost of addressing the risk outweighs its potential consequences. However, even when accepting a risk, it is important to monitor and have contingency plans in place if the risk materializes.
B. Developing risk response plans.
Once risk response strategies are determined, it is essential to develop detailed risk response plans for each identified risk. These plans provide a roadmap for implementing the chosen risk response strategies. The following elements should be included in the risk response plans:
- Actionable steps for each identified risk: Clearly outline the specific actions and measures that will be taken to implement the chosen risk response strategy. This includes detailed instructions on what needs to be done, who is responsible, and when the actions should be executed.
- Allocating resources and responsibilities: Identify the necessary resources, such as budget, manpower, and tools, required to implement the risk response plans. Assign clear responsibilities to team members or stakeholders involved in executing the plans. This ensures accountability and effective coordination throughout the risk response process.
By developing comprehensive risk response plans, project teams can effectively address identified risks and minimize their potential impact. Clear and actionable steps, along with allocated resources and responsibilities, facilitate the execution of risk response strategies, enhancing the project’s ability to navigate uncertainties and achieve successful outcomes.
V. Risk Monitoring and Control
A. Establishing risk monitoring mechanisms.
To effectively manage project risks, it is essential to establish robust risk monitoring mechanisms. These mechanisms enable ongoing assessment and control of identified risks throughout the project lifecycle. The following strategies can be implemented:
- Regular risk assessments: Conduct periodic risk assessments to review the status of identified risks, reassess their probability and impact, and identify any new risks that may have emerged. Regular assessments help in staying proactive and responsive to evolving risks. This can be done through structured meetings, check-ins with the project team, or utilizing risk management software tools.
- Tracking risk indicators: Define and track key risk indicators or metrics that provide insights into the status of risks. These indicators can be qualitative or quantitative, such as the number of incidents, deviation from project milestones, or cost variances. By monitoring these indicators, early warning signs of potential risks can be identified, allowing for timely intervention and mitigation.
B. Implementing risk control measures
Risk control measures aim to mitigate or eliminate identified risks. Once risks are monitored, appropriate actions should be taken to control and manage them effectively. The following steps are crucial in implementing risk control measures:
- Taking corrective actions: When risks are identified or when risk indicators suggest an escalating risk, it is important to take prompt corrective actions. This may involve revising project plans, reallocating resources, adjusting timelines, or implementing additional safety measures. The actions should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), allowing for effective risk mitigation.
- Adjusting the project plan as needed: As risks are addressed and new information becomes available, it may be necessary to adjust the project plan. This can include revising schedules, budgets, or resource allocations to accommodate risk response activities. Regularly review and update the project plan to reflect the evolving risk landscape and ensure alignment with risk mitigation efforts.
By establishing robust risk monitoring mechanisms and implementing effective risk control measures, project teams can actively monitor and respond to risks in a timely manner. Regular risk assessments and tracking of risk indicators help in staying proactive, while taking corrective actions and adjusting the project plan ensure that risks are effectively managed throughout the project lifecycle.
VI. Risk Communication and Reporting
A. Communicating risks to stakeholders.
Effective communication of project risks to stakeholders is vital for maintaining transparency, managing expectations, and obtaining necessary support. The following strategies can enhance risk communication:
- Clear and concise reporting: Present risks in a clear and easily understandable manner, using concise language and avoiding technical jargon. Provide relevant information about each risk, including its potential impact, likelihood, and proposed risk response strategies. Utilize visual aids such as charts or graphs to enhance clarity and facilitate comprehension.
- Timely updates on risk status: Regularly update stakeholders on the status of identified risks. Communicate any changes in the risk landscape, new risks that have emerged, or updates on the progress of risk mitigation efforts. Timeliness in sharing risk information helps stakeholders stay informed and enables them to make informed decisions and adjustments as needed.
B. Engaging stakeholders in risk management.
Engaging stakeholders in the risk management process fosters a sense of ownership and collective responsibility. The following approaches can promote stakeholder involvement:
- Soliciting feedback and suggestions: Encourage stakeholders to provide their input and insights on identified risks. Actively seek feedback on risk response strategies, potential mitigation measures, or any additional risks that stakeholders may have identified. This collaborative approach enhances the overall effectiveness of risk management by leveraging diverse perspectives and expertise.
- Encouraging proactive risk identification: Create an environment that encourages stakeholders to proactively identify and report potential risks. Establish channels for stakeholders to raise concerns or share information related to project risks. This can include anonymous reporting mechanisms or regular risk review meetings where stakeholders can freely express their views. Recognize and reward proactive risk identification to incentivize stakeholder engagement.
By communicating risks effectively and engaging stakeholders in the risk management process, project teams can foster a culture of transparency, collaboration, and collective ownership. Clear and concise reporting ensures stakeholders are well-informed, while timely updates keep them abreast of the evolving risk landscape. Engaging stakeholders through feedback and proactive risk identification strengthens risk management practices and enhances the overall success of the project.
VII. Contingency Planning
A. Developing contingency plans.
Contingency planning involves developing alternate strategies to address potential risks and ensure project continuity. It provides a proactive approach to deal with unforeseen events. The following steps are crucial in developing effective contingency plans:
- Identifying alternative courses of action: Analyze each identified risk and develop alternative approaches or plans to mitigate the impact if the risk materializes. These alternative courses of action should be well-defined, feasible, and aligned with the project objectives. Consider different scenarios and devise strategies that can be implemented swiftly and effectively.
- Preparing for potential risk occurrences: Anticipate the potential consequences of identified risks and prepare appropriate responses. This may include preparing backup resources, establishing communication protocols, securing additional funding, or developing mitigation strategies. Contingency plans should outline specific actions, responsibilities, and necessary resources required to implement them.
B. Trigger points and response activation
To ensure timely execution of contingency plans, it is essential to establish trigger points and define the conditions under which the plans should be activated. The following steps can facilitate effective trigger point determination:
- Determining thresholds for activating contingencies: Establish clear criteria or thresholds that indicate when a risk has escalated to a level where the contingency plan should be activated. These thresholds can be based on factors such as the severity of the risk, the potential impact on project objectives, or specific project performance indicators. Ensure that trigger points are defined objectively and in alignment with the risk assessment and overall project goals.
- Ensuring timely execution of contingency plans: Once the trigger points are reached, activate the appropriate contingency plans promptly. This involves communicating the activation to the relevant stakeholders, assigning responsibilities, and implementing the pre-defined actions outlined in the contingency plans. Timely execution is crucial to minimize the impact of risks and ensure project progress remains on track.
By developing comprehensive contingency plans and defining trigger points for their activation, project teams are better prepared to respond to unexpected events or risk occurrences. The identification of alternative courses of action and preparation for potential risk occurrences helps mitigate the impact on project objectives. Timely execution of contingency plans ensures swift response and reduces potential disruptions, enhancing project resilience and success.
VIII. Lessons Learned and Continuous Improvement
A. Conducting post-project risk reviews.
Post-project risk reviews provide valuable insights and opportunities for learning from the project experience. The following steps contribute to effective post-project risk reviews:
- Evaluating the effectiveness of risk management strategies: Reflect on the outcomes of risk management strategies implemented during the project. Assess whether the chosen risk response plans were effective in mitigating or addressing identified risks. Analyze the overall performance of the risk management process and identify areas for improvement.
- Documenting lessons learned for future projects: Capture key lessons learned from the project’s risk management process. Document successes, challenges, and areas where improvements could have been made. This information serves as a knowledge repository for future projects, enabling project teams to build upon previous experiences and avoid repeating mistakes.

B. Incorporating feedback into future risk management practices.
To continuously improve risk management practices, it is important to incorporate feedback from stakeholders and project team members. The following approaches can facilitate this process:
- Updating risk management processes and tools: Based on lessons learned and feedback, update risk management processes and methodologies to enhance their effectiveness. Revise risk identification techniques, risk assessment frameworks, or risk response strategies as necessary. Incorporate new industry standards, best practices, and emerging tools to stay current with evolving risk management practices.
- Promoting a culture of proactive risk management: Foster a culture where proactive risk management is encouraged and valued. Establish channels for stakeholders and team members to provide feedback on the risk management process. Encourage open communication, knowledge sharing, and continuous learning regarding risk management. Recognize and reward individuals who demonstrate proactive risk identification and effective risk response.
By conducting post-project risk reviews and incorporating feedback into risk management practices, project teams can drive continuous improvement. Evaluating the effectiveness of risk management strategies and documenting lessons learned enables future projects to benefit from past experiences. Updating risk management processes and tools, along with promoting a culture of proactive risk management, contributes to ongoing enhancement of risk management capabilities within the organization.
IX. Conclusion
A. Recap of project risk management principles and practices
Project risk management is a critical process that involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to ensure project success. Throughout the project lifecycle, several key principles and practices contribute to effective risk management. These include:
- Risk identification: Identifying various types of risks, including internal, external, technical, and organizational risks.
- Risk assessment and analysis: Conducting qualitative and quantitative analysis to evaluate the probability, impact, and prioritization of risks.
- Risk response planning: Developing strategies such as avoidance, mitigation, transfer, or acceptance to address identified risks.
- Risk monitoring and control: Establishing mechanisms to monitor risks, track risk indicators, and implementing timely risk control measures.
- Risk communication and reporting: Effectively communicating risks to stakeholders through clear and concise reporting, and engaging stakeholders in risk management through feedback and proactive risk identification.
- Contingency planning: Developing contingency plans with alternative courses of action and trigger points for activation to address potential risk occurrences.
- Lessons learned and continuous improvement: Conducting post-project risk reviews, documenting lessons learned, and incorporating feedback to enhance risk management practices.
B. Emphasizing the importance of ongoing risk management throughout the project lifecycle.
Ongoing risk management is crucial for project success. Risks are dynamic and can change over time, requiring continuous monitoring and proactive management. By integrating risk management practices throughout the project lifecycle, organizations can better anticipate, assess, and respond to risks. This proactive approach helps prevent or mitigate potential disruptions, delays, or cost overruns.
Maintaining a focus on risk management throughout the project lifecycle enables project teams to identify emerging risks, adapt risk response strategies, and ensure that project objectives are achieved. It also promotes a culture of risk awareness and proactive risk identification, enhancing the overall resilience and success of projects.
In conclusion, project risk management is an essential discipline that enables organizations to effectively navigate uncertainties and ensure project success. By implementing the principles and practices outlined in this outline, project teams can identify, assess, and mitigate risks, fostering a proactive and resilient approach to project management.



